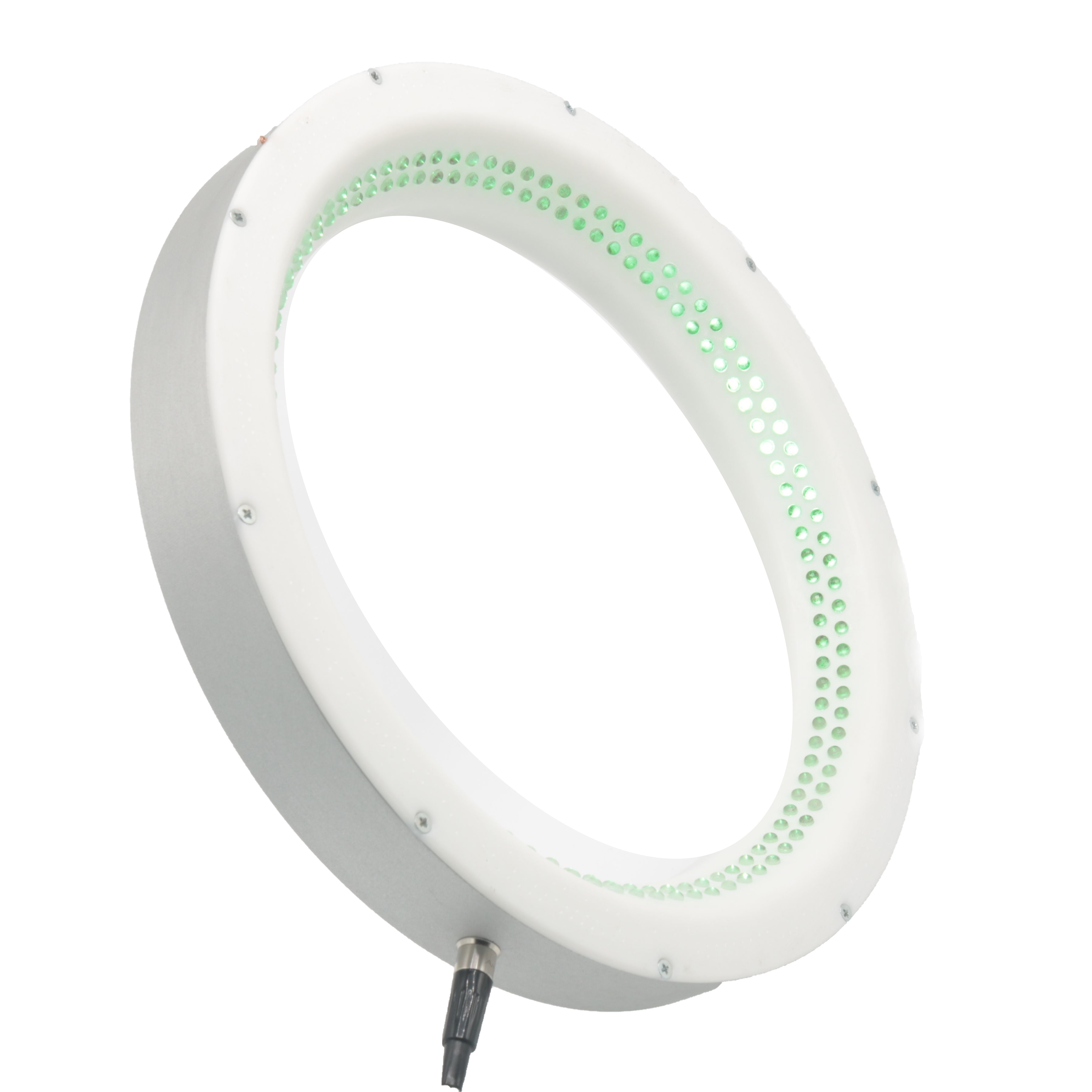
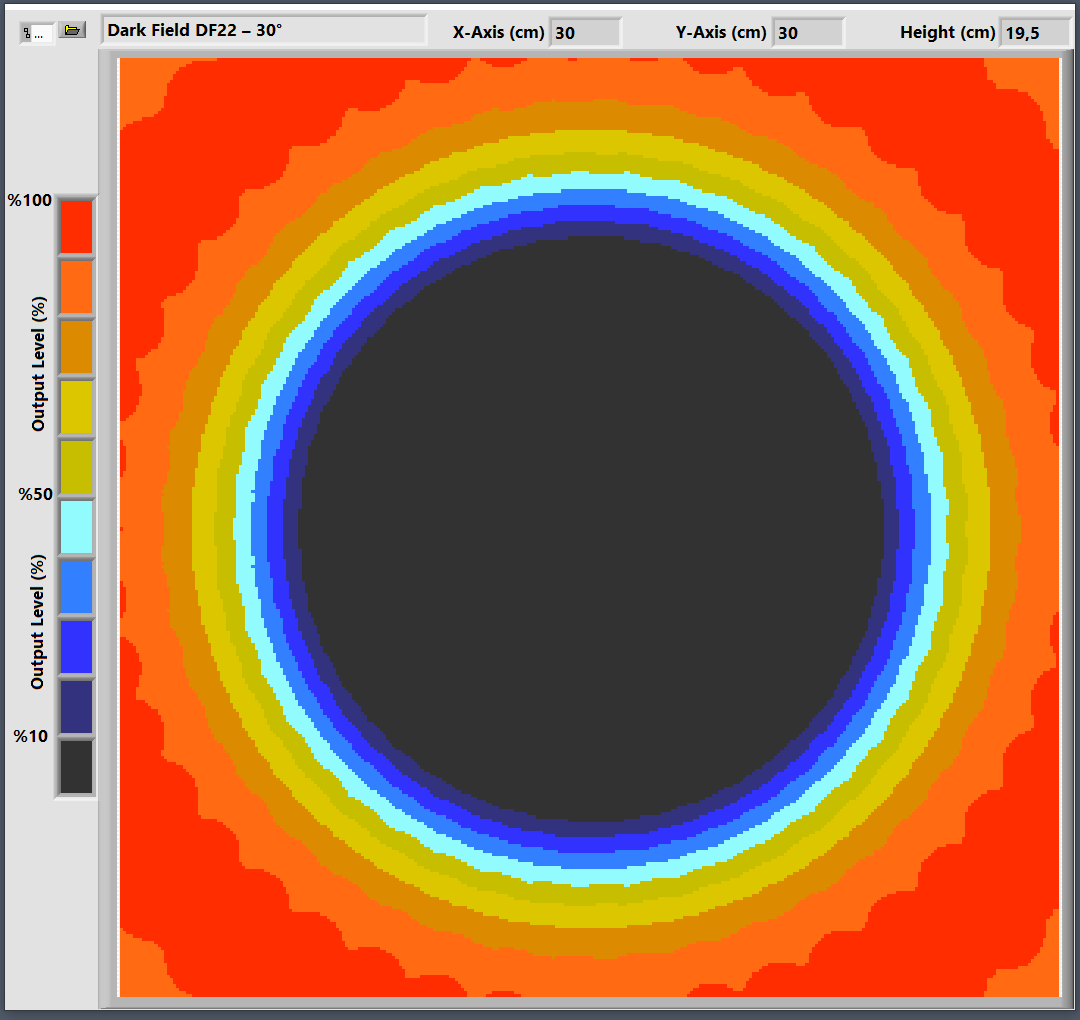
Low Angle DFL220-30
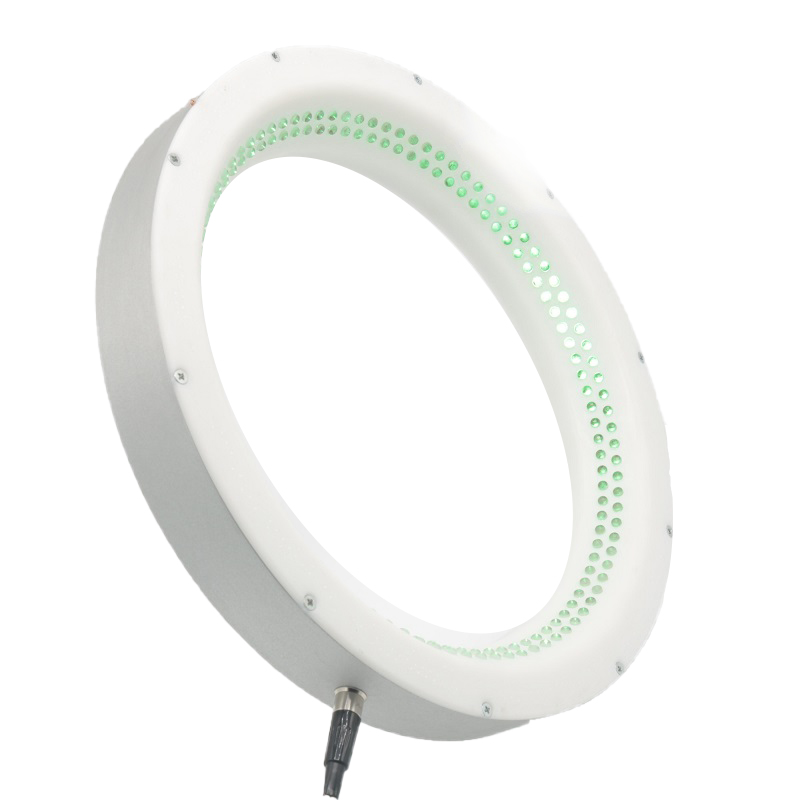

LUDRE DARK FIELD LIGHT DF25 MACHINE VISION IMAGE PROCESSING LIGHT
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Lighting Color: 6000K, Green
Illumination Angle: 30°
Illumination Intensity: 0.225 lm
Number of LEDs: 90
Input Voltage: 24 V
Input Current (15 µs): 2 A
Input Current (1 second): 1,4 A
Input Current (1 minute): 0,7 A
Input Current (continuous): 0,32 A
Dimensions: Rmin = 22 cm, Rmax = 29 cm, h = 3.8 cm
Stable Voltage Operation: No
Diffuser Option: No
PRION RING LIGHT (DARK FIELD) MACHINE VISION IMAGE PROCESSING LIGHT
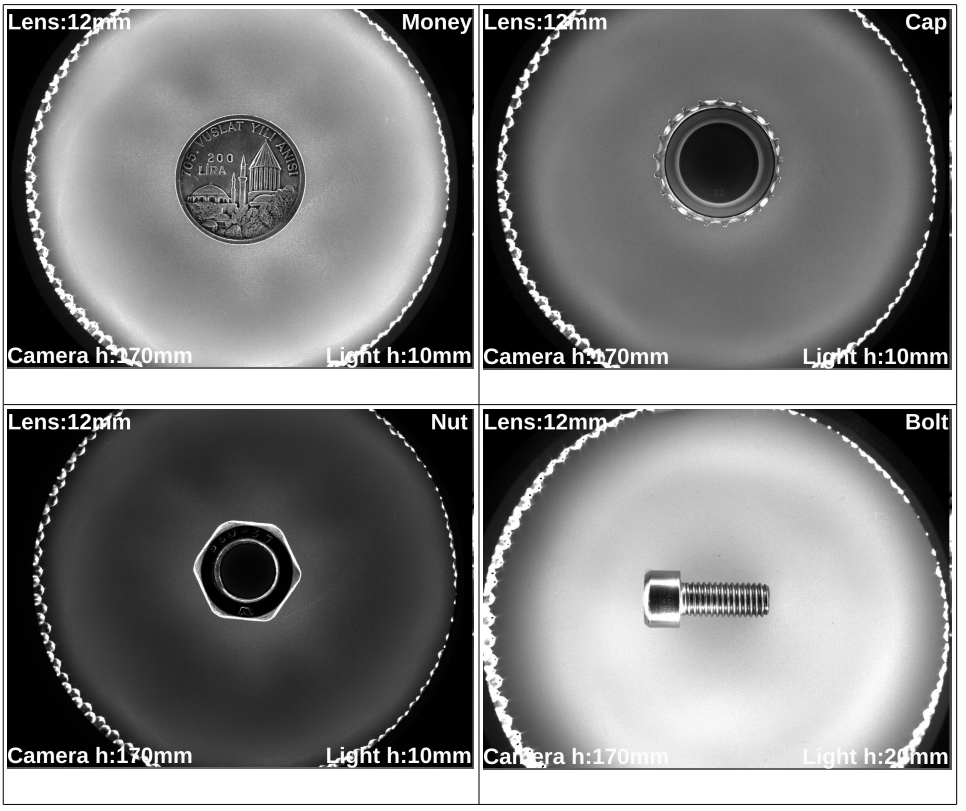
Ring Light is a specialized light source used in industrial image processing systems, providing even and shadow-free illumination. Its circular (uniformly round) structure allows the light source to be positioned around the camera, ensuring the light is distributed evenly from all angles onto the object. This eliminates shadows on the object, resulting in clearer and more detailed images. Ring Light is particularly ideal for inspecting small, delicate objects and applications that require high contrast.
Ring Light is commonly used in quality control for sensitive products such as electronic components, optical devices, dental products, jewelry, and pharmaceuticals. By providing high contrast, it enhances the visibility of small texts, labels, and markings. It is also highly effective for detecting surface roughness and defects.
Ring Light completely eliminates shadows, ensuring that every detail on the surface is clearly visible. With even light distribution, it provides homogeneous lighting across all areas and minimizes sensitivity to reflections. This makes it especially advantageous for inspecting optical and electronic components.
.png)
The Ring Light is a lighting solution used in machine vision systems across various industries, including part inspection, plastics, glass, textiles, automotive, and electronics, providing homogeneous and shadow-free illumination. It is ideal for detecting surface defects in metal, plastic, and other materials, identifying edge flaws in transparent and semi-transparent plastics, and revealing scratches or cracks on glass surfaces. In the textile industry, it helps detect thread defects, color inconsistencies, and printing errors, while in the automotive sector, it is used for inspecting surface quality and detecting paint defects. In electronics and PCB inspection, it plays a crucial role in identifying soldering defects and component assembly errors on printed circuit boards. Its circular design focuses light on a central point, minimizing reflections and enhancing contrast, ultimately optimizing quality control processes.
.png)